What is Moksha?
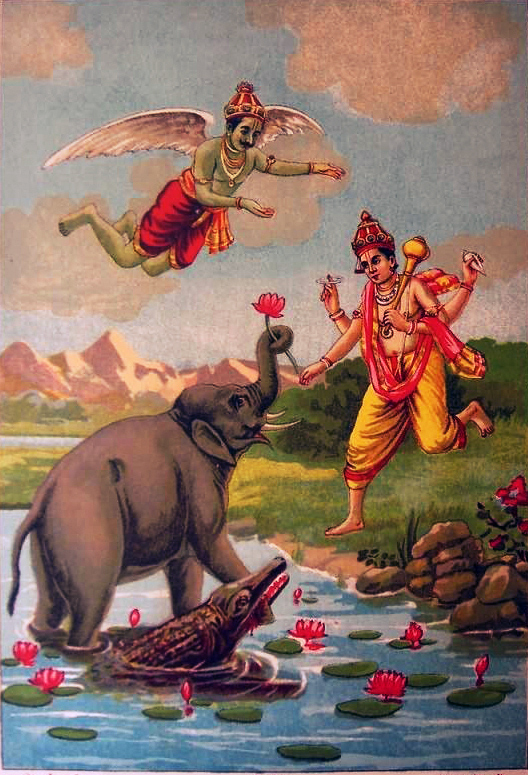
Moksha (Sanskrit for "liberation") is the highest goal of life in the Hindu religion. Also known as mukti (release), moksha refers to the sumum bonum of Hindu thought in which one's soul is freed from the karmic suffering of the samsaric world. In higher Hindu philosophy, it is seen as a transcendence of phenomenal being, and an escape from all limitations entailed in embodied worldly existence, including any sense of consciousness of time, space, and causation (karma). It signifies the dissolution of the sense of self as an egoistic personality—the undoing of conditioned mentality-materiality or nama-rupa (name-form). During moksha, one allegedly gains self-realization and complete awareness of ultimate reality.
Hinduism provides a number of spiritual paths for a practitioner to attain moksha, allowing such diversity for various types of people. However, it is said that the attainment of moksha is very rare and countless reincarnations are required for a person to reach this state of spiritual perfection. Some Hindu schools restrict the attainment of moksha to males only, while others claim that moksha is available to anyone who demonstrates the requisite effort and/or devotion. In some ways the Hindu concept of moksha resembles the Christian idea of salvation but the two concepts are incommensurate because they are based on different underlying presuppositions about reality.
Hinduism views mankind as divine. Because Brahma is everything, Hinduism asserts that everyone is divine. Atman, or self, is one with Brahman. All of reality outside of Brahman is considered mere illusion. The spiritual goal of a Hindu is to become one with Brahma, thus ceasing to exist in its illusory form of "individual self." This freedom is referred to as "moksha." Until moksha is achieved, a Hindu believes that he/she will be repeatedly reincarnated in order that he/she may work towards self-realization of the truth (the truth being that only Brahman exists, nothing else). How a person is reincarnated is determined by karma, which is a principle of cause and effect governed by nature's balance. What one did in the past affects and corresponds with what happens in the future, past and future lives included.
What is the difference between Nirvana and Moksha?
Both Hinduism and Buddhism focus on liberation from the endless cycle of samsara - the endless cycle of birth and death, and the suffering that comes with that cycle.
There are, however, important distinctions in how the two traditions view this liberation.
In Hinduism, this liberation is known as "moksha." This term literally means "release" in the sense of "letting go." Moksha is the letting go of the repeated birth and death of the physical body - reincarnation. Because Hindu teaching includes the notion of a soul, or "atman," when someone attains moksha, their soul merges with Brahman - the source of all existence.
In Buddhism, liberation from samsara is known as "nirvana." This term literally means "extinction" or "blowing out," in the sense of extinguishing a burning flame. In Buddhist teaching, humans are bound to samsara through the flames of anger, ignorance and desire. So in Buddhism, when one attains nirvana, one extinguishes anger, ignorance and desire.
This is a subtle and tricky point - in Buddhism, humans escape life and death by extinguishing anger, ignorance and desire, even though the physical body may still be alive (death is not a prerequisite for nirvana). This is why Buddhists talk of rebirth rather than reincarnation.
A Buddhist who has attained nirvana is untethered from anger (which focuses on the past), ignorance (which focuses on the present) and desire (which focuses on the future). Nirvana is the extinction of time, and since life and death are bound by time, nirvana is the freedom from life and death.
The ultimate objective of all reincarnation is to fuse with "ultimate reality", to merge with God, to become "God". All reincarnation teachings are based on a monistic, mystical - occult world view that promotes the essential divinity of humanity, denies the notion of a sovereign personal God, and offers the promise of esoteric wisdom.
Related articles: